NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter-8 (Application Of Integrals)Exercise 8.2
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths from class
12th Students will get the answers of
Chapter-8 (Application Of Integrals)Exercise 8.2 This chapter will help you to learn the basics and you should expect at least one question in your exam from this chapter.
We have given the answers of all the questions of
NCERT Board Mathematics Textbook in very easy language, which will be very easy for the students to understand and remember so that you can pass with good marks in your examination.
Exercise 8.2
Q1. Find the area of the circle 4x2+4y2=9 which is interior of the parabola x2=4y
Answer. The required area is represented by the shaded area OBCDO. 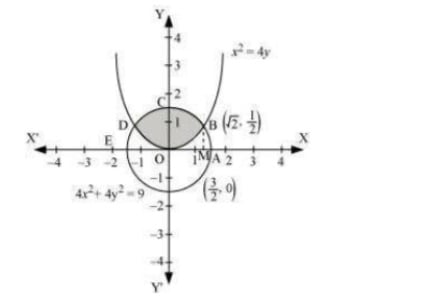 Solving the given equation of circle, 4x2+4y2=9, and parabola, x2=4y, we obtain the point of intersection as (√2,12) and D(−√2,12) It can be observed that the required area is symmetrical about y-axis. ∴ Area OBCDO = 2× Area OBCO We draw BM perpendicular to OA. Therefore, the coordinates of M are (√2,0) . Therefore, Area OBCO = Area OMBCO - Area OMBO =∫√20√(9−4x2)4dx−∫√x24dx=12∫√20√9−4x2dx−14∫√20x2dx=14[x√9−4x2+92sin−12x3]√20−14[x33]√20 =14[√2√9−8+92sin−12√23]−112(√2)3=√24+98sin−12√23−√26=√212+98sin−12√23=12(√26+94sin−12√23) Therefore, the required area OBCDO is (2×12[√26+94sin−12√23])=[√26+94sin−12√23] units
Solving the given equation of circle, 4x2+4y2=9, and parabola, x2=4y, we obtain the point of intersection as (√2,12) and D(−√2,12) It can be observed that the required area is symmetrical about y-axis. ∴ Area OBCDO = 2× Area OBCO We draw BM perpendicular to OA. Therefore, the coordinates of M are (√2,0) . Therefore, Area OBCO = Area OMBCO - Area OMBO =∫√20√(9−4x2)4dx−∫√x24dx=12∫√20√9−4x2dx−14∫√20x2dx=14[x√9−4x2+92sin−12x3]√20−14[x33]√20 =14[√2√9−8+92sin−12√23]−112(√2)3=√24+98sin−12√23−√26=√212+98sin−12√23=12(√26+94sin−12√23) Therefore, the required area OBCDO is (2×12[√26+94sin−12√23])=[√26+94sin−12√23] units
Q2. Find the area bounded by curves (x−1)2+y2=1 and x2+y2=1
Answer. The area bounded by the curves, (x−1)2+y2=1 and x2+y2=1, is represented by the shaded area as 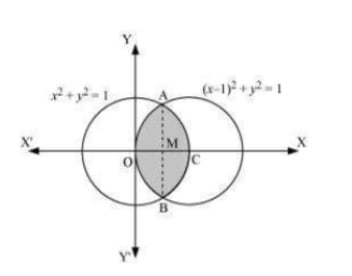 On solving the equations, (x−1)2+y2=1 and x2+y2=1, we obtain the point of intersection as A(12,√32) It can be observed that the required area is symmetrical about x-axis. ∴ Area OBCAO =2× Area OCAO We join AB, which intersects oC at M, such that AM is perpendicular to oc. The coordinates of M are (12,0) ⇒ Area OCAO= Area OMAO+Area MCAM =[∫120√1−(x−1)2dx+∫112√1−x2dx]=[x−12√1−(x−1)2+12sin−1(x−1)]120+[x2√1−x2+12sin−1x]112=⎡⎣−14√1−(−12)2+12sin−1(12−1)−12sin−1(−1)⎤⎦+ [12sin−1(1)−14√1−(12)2−12sin−1(12)] =[−√38+12(−π6)−12(−π2)]+[12(π2)−√38−12(π6)]=[−√34−π12+π4+π4−π12]+[12(π2)−√38−12(π6)]=[−√34−π6+π2]=[2π6−√34] Therefore ,required area OBCAO =2×(2π6−√34)=(2π3−√32) units
On solving the equations, (x−1)2+y2=1 and x2+y2=1, we obtain the point of intersection as A(12,√32) It can be observed that the required area is symmetrical about x-axis. ∴ Area OBCAO =2× Area OCAO We join AB, which intersects oC at M, such that AM is perpendicular to oc. The coordinates of M are (12,0) ⇒ Area OCAO= Area OMAO+Area MCAM =[∫120√1−(x−1)2dx+∫112√1−x2dx]=[x−12√1−(x−1)2+12sin−1(x−1)]120+[x2√1−x2+12sin−1x]112=⎡⎣−14√1−(−12)2+12sin−1(12−1)−12sin−1(−1)⎤⎦+ [12sin−1(1)−14√1−(12)2−12sin−1(12)] =[−√38+12(−π6)−12(−π2)]+[12(π2)−√38−12(π6)]=[−√34−π12+π4+π4−π12]+[12(π2)−√38−12(π6)]=[−√34−π6+π2]=[2π6−√34] Therefore ,required area OBCAO =2×(2π6−√34)=(2π3−√32) units
Q3. Find the area of the region bounded by the curves y=x2+2,y=x,x=0 and x=3
Answer. The area bounded by the curves, y=x2+2,y=x,x=0, and x=3, is represented by the shaded area OCBAO as 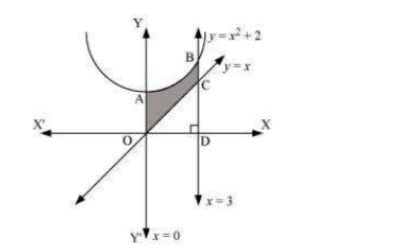 Then, Area OCBAO= Area ODBAO - Area ODCO =∫30(x2+2)dx−∫30xdx=[x33+2x]30−[x22]30 =[9+6]−[92]=15−92=212 units
Then, Area OCBAO= Area ODBAO - Area ODCO =∫30(x2+2)dx−∫30xdx=[x33+2x]30−[x22]30 =[9+6]−[92]=15−92=212 units
Q4. Using integration finds the area of the region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (−1,0),(1,3) and (3,2)
Answer. BL and CM are drawn perpendicular to x -axis. It can be observed in the following figure that, Area (ΔACB)= Area (ALBA)+ Area (BLMCB)− Area (AMCA)…(1) 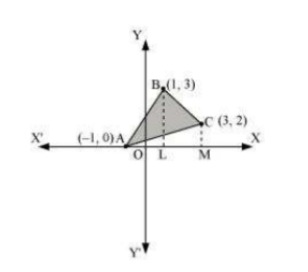 Equation of line segment AB is y−0=3−01+1(x+1)y=32(x+1)∴ Area (ALBA)=∫+−132(x+1)dx=32[x22+x]1−1=32[12+1−12+1]=3 units Equation of line segment BC is y−3=2−33−1(x−1)y=12(−x+7)∴ Area (BLMCB)=∫3112(−x+7)dx=12[−x22+7x]31=12[−92+21+12−7]=5 units Equation of line segment AC is y−0=2−03+1(x+1)y=12(x+1)∴ Area (AMCA)=12∫31(x+1)dx=12[x22+x]3−1=12[92+3−12+1]=4 units Therefore, from equation (1), we obtain Area (ΔABC) =(3+5−4)=4 units
Equation of line segment AB is y−0=3−01+1(x+1)y=32(x+1)∴ Area (ALBA)=∫+−132(x+1)dx=32[x22+x]1−1=32[12+1−12+1]=3 units Equation of line segment BC is y−3=2−33−1(x−1)y=12(−x+7)∴ Area (BLMCB)=∫3112(−x+7)dx=12[−x22+7x]31=12[−92+21+12−7]=5 units Equation of line segment AC is y−0=2−03+1(x+1)y=12(x+1)∴ Area (AMCA)=12∫31(x+1)dx=12[x22+x]3−1=12[92+3−12+1]=4 units Therefore, from equation (1), we obtain Area (ΔABC) =(3+5−4)=4 units
Q5. Using integration find the area of the triangular region whose sides have the equations y=2x+1,y=3x+1 and x=4 .
Answer. The equations of sides of the triangle are y=2x+1,y=3x+1, and x=4 . On solving these equations, we obtain the vertices of triangle as A(0,1),B(4,13), and C(4,9). 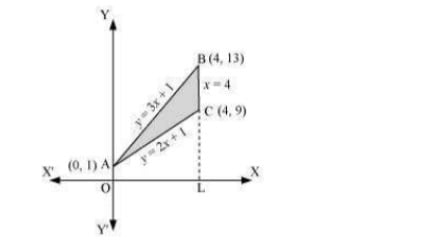 It can be observed that, Area (ΔACB)= Area (OLBAO) -Area (OLCAO) =∫40(3x+1)dx−∫40(2x+1)dx=[3x22+x]40−(2x22+x]40=28−20=8 units
It can be observed that, Area (ΔACB)= Area (OLBAO) -Area (OLCAO) =∫40(3x+1)dx−∫40(2x+1)dx=[3x22+x]40−(2x22+x]40=28−20=8 units
Q6. Smaller area enclosed by the circle x2+y2=4 and the line x+y=2 is A. 2(n−2) B. π−2 C. 2π−1 D. 2(n+2)
Answer. The smaller area enclosed by the circle, x2+y2=4, and the line, x+y=2, is represented by the shaded area ACBA as 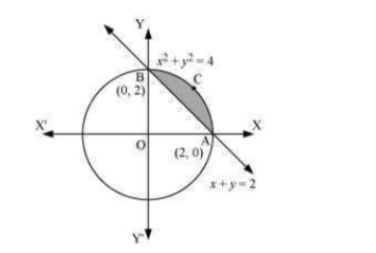 It can be observed that, Area ACBA= Area OACBO - Area (\DeltaOAB) =∫20√4−x2dx−∫20(2−x)dx =[x2√4−x2+42sin−1x2]20−[2x−x22]20=[2⋅π2]−[4−2]=(π−2)−[4−2]=(π−2) units Thus, the correct answer is B.
It can be observed that, Area ACBA= Area OACBO - Area (\DeltaOAB) =∫20√4−x2dx−∫20(2−x)dx =[x2√4−x2+42sin−1x2]20−[2x−x22]20=[2⋅π2]−[4−2]=(π−2)−[4−2]=(π−2) units Thus, the correct answer is B.
Q7. Area lying between the curve y2=4x and y=2x is A. 23 B. 13 C. 14 D. 34 C. 14 D. 34
Answer. The area lying between the curve, y2=4x and y=2x, is represented by the shaded area OBAO as 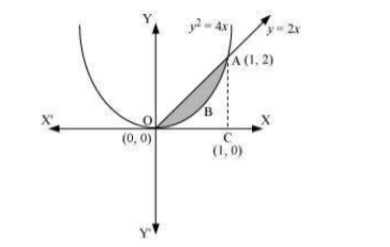 The points of intersection of these curves are 0(0,0) and A(1,2) . We draw AC perpendicular to x -axis such that the coordinates of C are (1,0) ∴ Area OBAO = Area (ΔOCA)− Area(OCABO) =∫402xdx−∫202√xdx=2[x22]10−2[x3232]10=∣∣1−43∣∣=∣∣−13∣∣=13 units Thus, the correct answer is B.
The points of intersection of these curves are 0(0,0) and A(1,2) . We draw AC perpendicular to x -axis such that the coordinates of C are (1,0) ∴ Area OBAO = Area (ΔOCA)− Area(OCABO) =∫402xdx−∫202√xdx=2[x22]10−2[x3232]10=∣∣1−43∣∣=∣∣−13∣∣=13 units Thus, the correct answer is B.
Chapter-8 (integrals)

 Therefore ,required area OBCAO
Therefore ,required area OBCAO 



 Area(OCABO)
Area(OCABO) 









